How many times in your life have you smashed one of your favourite mugs, plates or bowls? Sometimes it just slips out of your hands, other times time works its magic and one day a crack appears, the ear remains in your hand …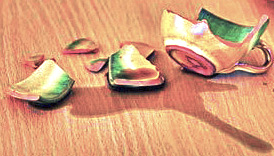
 If it is a very precious or favourite piece of yours and it has not cracked to too many shards, you might want to try to fix it so that it would not be visible repair. Then you can use such a mug, for example, for pencils, plate or bowl under the flower. But only if you can get it together in such way that it is not at first sight recognizable. Otherwise, you just throw it away.
If it is a very precious or favourite piece of yours and it has not cracked to too many shards, you might want to try to fix it so that it would not be visible repair. Then you can use such a mug, for example, for pencils, plate or bowl under the flower. But only if you can get it together in such way that it is not at first sight recognizable. Otherwise, you just throw it away.

But it can be done differently. You can on the contrary repair such a piece so its repair stands out, it is shining in the distance and making so a new original piece in its way.
In Japanese culture, you can find Kintsugi art (translated to “golden joinery”) or Kintsukuroi (“golden repair”) – which can be briefly described as an art of repairing broken ceramics with a lacquer dusted or mixed with gold, silver or even platinum powder. It is believed that sometimes the repair of broken things can make them even better and more beautiful than if they were new.
This way of repair celebrates the unique history of each artefact by emphasizing its breakages, cracks or even missing parts instead of hiding or disguising them. Kintsugi often makes the repaired piece even more beautiful than the original, reviving it with a new life.
History
 The art of Kintsugi dates back to the end of the 15th century. According to one legend, this art came into being when Japanese shogun Ashikaga Yoshimasa sent a cracked Chinese chawan (a tea bowl) back to China for a repair. After its return, Yoshimasa was disappointed to find that this was corrected by unsightly metal staples. This motivated his craftsmen to find an alternative, aesthetically pleasing method of repair. And so Kintsugi was born.
The art of Kintsugi dates back to the end of the 15th century. According to one legend, this art came into being when Japanese shogun Ashikaga Yoshimasa sent a cracked Chinese chawan (a tea bowl) back to China for a repair. After its return, Yoshimasa was disappointed to find that this was corrected by unsightly metal staples. This motivated his craftsmen to find an alternative, aesthetically pleasing method of repair. And so Kintsugi was born.
 Collectors were so enchanted by this new art that some were accused of deliberately breaking valuable pottery to repair it with the golden Kintsugi seams. Kintsugi became closely associated with the ceramic vessels used for the Japanese tea ceremony – the chanoyu. However, over time, this technique has also been applied to ceramic pieces of non-Japanese origin, including China, Vietnam and Korea.
Collectors were so enchanted by this new art that some were accused of deliberately breaking valuable pottery to repair it with the golden Kintsugi seams. Kintsugi became closely associated with the ceramic vessels used for the Japanese tea ceremony – the chanoyu. However, over time, this technique has also been applied to ceramic pieces of non-Japanese origin, including China, Vietnam and Korea.
Philosophy
 Since its inception, Kintsugi technique has been connected and influenced by various philosophical thoughts. Specifically, with Japanese philosophy wabi-sabi, which calls for beauty to be seen in flawed or imperfections. This way of repair is also associated with the Japanese feeling of mottainai, which expresses regret when something is useless or thrown away, as well as mushin – freedom from premature trials and presumptions.
Since its inception, Kintsugi technique has been connected and influenced by various philosophical thoughts. Specifically, with Japanese philosophy wabi-sabi, which calls for beauty to be seen in flawed or imperfections. This way of repair is also associated with the Japanese feeling of mottainai, which expresses regret when something is useless or thrown away, as well as mushin – freedom from premature trials and presumptions.
Basic methods
There are three predominant Kintsugi styles: crack repair, piece recovery method, and joint-call method. While, in any case, gold-dusted compound/epoxide is used to repair the broken ceramics, the remedies themselves differ a little from each other.
 Crack repair method – use of gold dust and resin or lacquer to fix broken pieces with minimal overlapping or filling of missing pieces
Crack repair method – use of gold dust and resin or lacquer to fix broken pieces with minimal overlapping or filling of missing pieces
 The piece recovery method – if a ceramic fragment is not available, it is produced and supplemented exclusively by epoxy resin – golden mixtures
The piece recovery method – if a ceramic fragment is not available, it is produced and supplemented exclusively by epoxy resin – golden mixtures
 Joint call method – the missing piece of ceramics is replaced by a similarly shaped but inconsistent fragment of aesthetically different ceramics. It combines two visually different works into one unique piece. It is a method reminiscent of the well-known patchwork.
Joint call method – the missing piece of ceramics is replaced by a similarly shaped but inconsistent fragment of aesthetically different ceramics. It combines two visually different works into one unique piece. It is a method reminiscent of the well-known patchwork.
Present time
Kintsugi inspires many artists and craftsmen all over the world even today. And it does keep this ancient tradition alive. Works inspired by this technique can be found in many world museums and galleries.
But it can also inspire us. The next time we will not want to throw away a crackled saucer from a grandmother’s set, a broken cup we liked, or just an old flower pot … We can also take the breaks and subsequent repair as part of the history of the object, rather than something that should be disguised.